curl
--header "Content-Type: text/xml;charset=UTF-8" --header
"SOAPAction:GetMSISDNList" --data @request.xml http://172.31.70.139:10037/serkans/SunelServices
--------------Content of the request.xml--------------
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:s="http://modafone.com.tr/Business/SerkanServices" xmlns:head="http://modafone.com.tr/EAI/Common/Header" xmlns:v1="http://modafone.com.tr/GetMSISDNList">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<s:GetMSISDNList>
<Header>
<head:RequestId>323488131</head:RequestId>
<head:SourceSystem>www</head:SourceSystem>
</Header>
<Body>
<v1:Request>
<v1:MSISDN>5444444440</v1:MSISDN>
</v1:Request>
</Body>
</s:GetMSISDNList>
</soapenv:Body>
Tuesday, November 17, 2015
Friday, June 12, 2015
Things to remember ... -- Submitting tasks to the ExecutorService (newFixedThreadPool )
In the Javadoc , it is written :
java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool : If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
Here it is said that "They will wait"..
This does not mean any waiting thread. It means tasks that are submitted will be waiting in a queue for processing.
Submitting the tasks is not a blocking operation. Fixed Thread Pool uses a unbounded queue to hold the submitted tasks.
Task Submitter Thread will not be blocked ...
And the code for copy & paste & run & bye ...
java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool : If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
Here it is said that "They will wait"..
This does not mean any waiting thread. It means tasks that are submitted will be waiting in a queue for processing.
Submitting the tasks is not a blocking operation. Fixed Thread Pool uses a unbounded queue to hold the submitted tasks.
Task Submitter Thread will not be blocked ...
And the code for copy & paste & run & bye ...
import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * Created by ssunel on 6/1/2015. */public class TaskSubmitTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); MyMonitorThread monitor = new MyMonitorThread((ThreadPoolExecutor) executor, 3); Thread monitorThread = new Thread(monitor); monitorThread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { Runnable worker = new WorkerThread("" + i); executor.execute(worker); } System.out.println("All tasks are submitted !!!"); executor.shutdown(); while (!executor.isTerminated()) { } System.out.println("Finished all threads"); } static class WorkerThread implements Runnable { private String command; public WorkerThread(String s){ this.command=s; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Command = "+command); processCommand(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End."); } private void processCommand() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public String toString(){ return this.command; } } static class MyMonitorThread implements Runnable { private ThreadPoolExecutor executor; private int seconds; private boolean run=true; public MyMonitorThread(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, int delay) { this.executor = executor; this.seconds=delay; } public void shutdown(){ this.run=false; } @Override public void run() { while(run){ System.out.println( String.format("[monitor] [%d/%d] Active: %d, Completed: %d, Task: %d, isShutdown: %s, isTerminated: %s, taskQueueSize: %d", this.executor.getPoolSize(), this.executor.getCorePoolSize(), this.executor.getActiveCount(), this.executor.getCompletedTaskCount(), this.executor.getTaskCount(), this.executor.isShutdown(), this.executor.isTerminated(), this.executor.getQueue().size())); try { Thread.sleep(seconds*1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
Wednesday, January 28, 2015
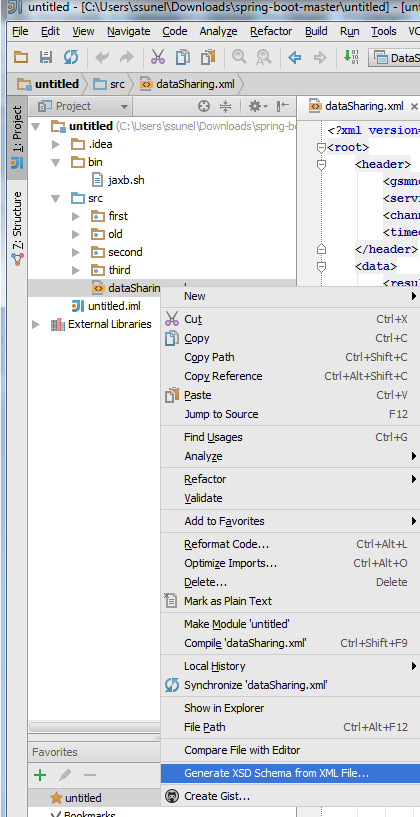
Generate XStream Classes
While dealing with XStream if you had to create mapper classes and write a parser you would want use a shortcut for solution.
For the next time i will follow the below path
1) Create xsd file for the given xml using IntelliJ Idea
2) Create Jaxb classes for the generated xsd file : http://goo.gl/uOjSAz
3) in the generated you need to put add : @XStreamAlias( "xml_tag_name_for_classs" ) for each class or attribute when you see the @XmlRootElement(name = "xml_tag_name_for_the _item_or_class")
this will remove all undefined field exceptions of the XStream
If you get duplicate field exception add the @XStreamImplicit for the related field in the class
(I use copy paste for this job and if you have selected the third item in the first step you will have only one java file and replacing annotations will be easier. I have tried the other 2 options too for you)
4) in the parser class you need to xstream.processAnnotations(Your_class_name.class); Otherwise XStream will not recognize your annotations..Somethings are stupid still waits commands to do its work :/
In the end Parser class will be something like below
public class DataSharingParser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
XStream xstream = new XStream(new DomDriver());
//xstream.autodetectAnnotations(true);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Header.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.SharingPercentageList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.DataShareOptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.DataShareOptionList.SubscriptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.Msg.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.Msg.Valuelist.class);
Path xmlPath = Paths.get("C:\\somewhere_in_there\\src", "your_lovely.xml");
byte[] wikiArray = Files.readAllBytes(xmlPath);
String asString = new String(wikiArray, "UTF-8");
Root root = (Root) xstream.fromXML(asString);
Root.Data data = root.getData();
...more parsing sources goes below...
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
Note: You may not trust the xstream.autodetectAnnotations(true); while using XStream-1.4.7 and java 1.7
For the next time i will follow the below path
1) Create xsd file for the given xml using IntelliJ Idea
2) Create Jaxb classes for the generated xsd file : http://goo.gl/uOjSAz
3) in the generated you need to put add : @XStreamAlias( "xml_tag_name_for_classs" ) for each class or attribute when you see the @XmlRootElement(name = "xml_tag_name_for_the _item_or_class")
this will remove all undefined field exceptions of the XStream
If you get duplicate field exception add the @XStreamImplicit for the related field in the class
(I use copy paste for this job and if you have selected the third item in the first step you will have only one java file and replacing annotations will be easier. I have tried the other 2 options too for you)
4) in the parser class you need to xstream.processAnnotations(Your_class_name.class); Otherwise XStream will not recognize your annotations..Somethings are stupid still waits commands to do its work :/
In the end Parser class will be something like below
public class DataSharingParser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
XStream xstream = new XStream(new DomDriver());
//xstream.autodetectAnnotations(true);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Header.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.SharingPercentageList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.DataShareOptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Data.CustomerDataShareOptionList.DataShareOptionList.SubscriptionList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.Msg.class);
xstream.processAnnotations(Root.Error.MsgList.Msg.Valuelist.class);
Path xmlPath = Paths.get("C:\\somewhere_in_there\\src", "your_lovely.xml");
byte[] wikiArray = Files.readAllBytes(xmlPath);
String asString = new String(wikiArray, "UTF-8");
Root root = (Root) xstream.fromXML(asString);
Root.Data data = root.getData();
...more parsing sources goes below...
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
Note: You may not trust the xstream.autodetectAnnotations(true); while using XStream-1.4.7 and java 1.7
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)